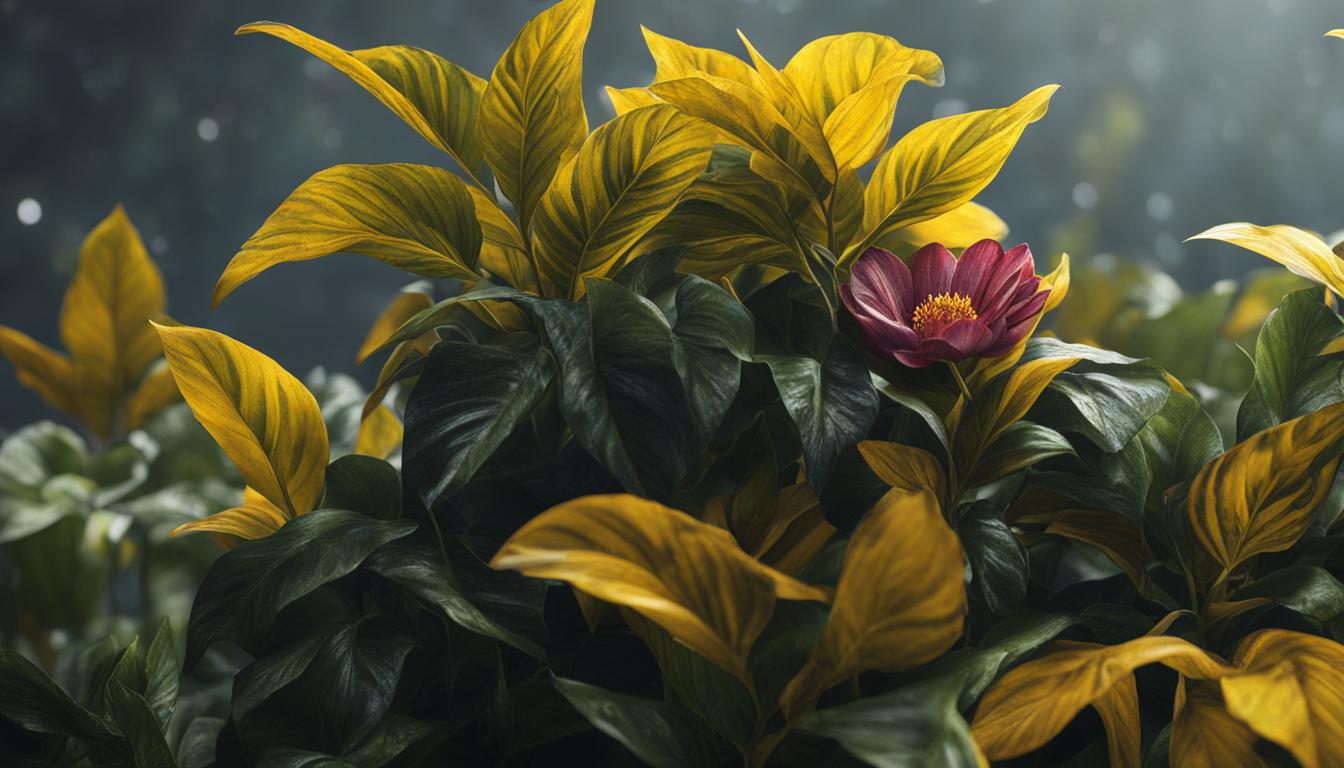

In this article, I’ll be diving into the world of plant virus symptoms and how to identify and diagnose them in your garden. It’s important to familiarize yourself with these symptoms, as early detection can help prevent the spread of diseases and protect your plants. So, let’s get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding plant virus symptoms is essential for the health of your garden.
- Common symptoms include color change, shape deformity, and altered function.
- Consider other possibilities before concluding a plant has a virus.
- Michigan State University Extension and Ohio State University provide helpful resources for identifying and controlling plant diseases.
- Early detection and prevention play a crucial role in managing plant virus symptoms.
Common Plant Virus Symptoms on Leaves
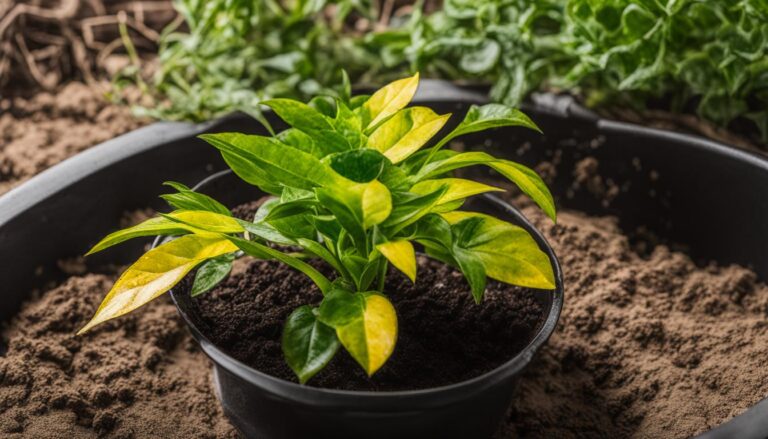
When it comes to plant virus symptoms, leaves often display noticeable signs of infection. These symptoms can manifest in various ways, including discoloration, distortion, and spotting.
Viral pathogens can cause irregular patterns of discoloration, resulting in leaves that appear yellowed, mottled, or with mosaic patterns. Other symptoms may include crinkling, wilting, or the development of leaf-like structures on infected flowers.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Leaf discoloration | Yellowing, mottling, or mosaic patterns on leaves |
| Leaf distortion | Crinkling, curling, or wilting of leaves |
| Leaf spotting | Development of small or large spots on leaves |
It is important to note that viral diseases cannot be visibly seen, and identification usually relies on identifying these distinct symptoms. When diagnosing plant virus symptoms on leaves, it is crucial to consider other possibilities, such as abiotic diseases or herbicide injury, before concluding that a plant has a virus.
Taking the time to properly identify the symptoms can help gardeners and growers take appropriate measures for disease control and management.
Plant Virus Symptoms on Fruit
When it comes to plant virus symptoms, it’s important not to overlook the impact on fruit. Viral infections can lead to discoloration, deformity, and spotting on the fruit, affecting both its appearance and quality. Identifying these symptoms is crucial for diagnosing and managing viral diseases that can impact fruit-bearing plants.
Common plant virus symptoms on fruit include the development of small yellow or brownish spots or blotches. Infected fruit may also show discoloration, distortion, streaks, or stunted growth.
In some cases, viral infections can result in the formation of irregular patterns, such as rings or mosaic patterns, on the fruit. These symptoms can be visually striking and serve as clear indicators of viral diseases affecting the fruit.
To provide a comprehensive understanding of the plant virus symptoms on fruit, here is a table summarizing some specific examples:
| Viral Disease | Symptoms on Fruit |
|---|---|
| Tomato spotted wilt virus | Fruit ringspots, mottling |
| Cucumber mosaic virus | Yellowing, green leaflike structures on fruit |
| Potato virus Y | Deformed or misshapen fruit |
By carefully observing and documenting these symptoms, gardeners and growers can take appropriate measures to manage viral diseases and prevent further spread. Proper sanitation practices, such as removing and destroying infected fruit, can help limit the impact of viral infections on fruit-bearing plants.
Plant Virus Symptoms on Flowers
When it comes to plant virus symptoms, flowers can display a range of visual indications. Flower discoloration, deformity, and spotting are common signs of viral infections.
Infected flowers may exhibit irregular patterns of discoloration or show alterations in shape and structure. These symptoms can significantly impact the overall appearance and health of flowering plants.
Examples of flower symptoms caused by viral diseases include chlorotic ringspots, necrotic ringspots, or the development of leaf-like structures on flowers. These visual cues can help gardeners and growers identify the presence of viral infections in their flowering plants.
It’s important to note that viral diseases cannot be visibly seen, and diagnosis usually relies on identifying the symptoms they cause.
Understanding plant virus symptoms on flowers is crucial in effectively managing and preventing the spread of viral infections. By recognizing these visual cues, gardeners and growers can take appropriate measures to control the spread of viruses and minimize their impact on flowering plants.

| Common Symptoms on Flowers | Causes |
|---|---|
| Chlorotic ringspots | Viral infections |
| Necrotic ringspots | Viral infections |
| Leaf-like structures on flowers | Viral infections |
Diagnosing Plant Virus Symptoms
Diagnosing plant virus symptoms involves careful observation and analysis of the visible effects on plants. When identifying plant virus symptoms, it is important to distinguish between signs and symptoms.
Signs refer to physical evidence of the pathogen, such as fungal fruiting bodies or bacterial exudate, while symptoms are the visible effects of the disease on the plant, such as changes in color, shape, or function.
While symptoms can overlap among fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases, understanding the unique patterns and characteristics can aid in diagnosis. For example, leaf rust, powdery mildew, leaf spot, and mosaic leaf patterns are common symptoms of fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases.
It is crucial to consider other factors such as abiotic diseases, herbicide injury, or nematode problems before concluding that a plant has a virus.
Michigan State University Extension and Ohio State University provide valuable resources for identifying and controlling plant diseases. Their publications, online information, and lab services can assist in diagnosing diseased plant samples.
By accessing these resources, gardeners and growers can gain knowledge in plant disease identification and take effective measures for disease control and management.
Diagnosing Plant Virus Symptoms – Summary:
- Diagnosing plant virus symptoms involves observing visible effects on plants.
- Signs refer to physical evidence of the pathogen, while symptoms are visible effects on the plant.
- Understanding unique patterns and characteristics aids in diagnosis.
- Consider other factors before concluding a plant has a virus.
- Michigan State University Extension and Ohio State University provide resources for plant disease identification and control.
Common Symptoms of Plant Virus Diseases
| Plant Part | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Leaves | Leaf rust, powdery mildew, leaf spot, mosaic leaf pattern |
| Fruit | Fruit discoloration, deformity, spotting, ringspots, mottling |
| Flowers | Flower discoloration, deformity, spotting, alterations in shape or structure |
Managing Plant Virus Symptoms
When it comes to plant virus symptoms, effective management is key to controlling the spread of viruses and minimizing their impact on your plants. While there is no cure or treatment for virus-infected plants in landscapes, there are steps you can take to improve plant vigor and prevent further infection.
One important aspect of managing plant virus symptoms is to purchase and plant high-quality, certified virus-free or virus-resistant nursery stock or seeds. This ensures that you are starting off with healthy plants that are less susceptible to viral infections.
It’s essential to avoid grafting virus-infected plant parts onto healthy plants, as this can introduce the virus to previously healthy specimens.
Controlling insects that can transmit plant viruses can also help prevent infection. It’s important to note that insect control is generally not effective for woody landscape plants.
Prevention and early detection play key roles in managing plant virus symptoms, so regular monitoring of your plants for any signs of infection is crucial.

By following these measures and implementing proper cultural care, you can help improve your plants’ resistance to viruses and minimize the impact of plant virus symptoms on your garden.
Types of Plant Virus Symptoms
Plant virus symptoms can manifest in various ways, depending on the affected plant part. Understanding these different types of symptoms is essential for diagnosing specific viral diseases and understanding their impact on plant health.
Leaf Symptoms
Leaf symptoms caused by viral diseases include discoloration, deformation, spotting, and wilting. Infected leaves may exhibit yellowing, crinkling, mosaic patterns, or stunted growth. Examples of leaf symptoms include leaf rust, powdery mildew, leaf spot, and mosaic leaf patterns.
Fruit Symptoms
Fruit symptoms caused by viral diseases include discoloration, deformity, spotting, ringspots, and mottling. Infected fruits may show small yellow or brownish spots, streaks, or stunted growth. Examples of fruit symptoms include fruit spots, fruit ringspots, and fruit mottling.
Flower Symptoms
Flower symptoms caused by viral diseases can result in discoloration, deformation, spotting, or alterations in shape or structure. Infected flowers may develop chlorotic ringspots, necrotic ringspots, or leaf-like structures. Examples of flower symptoms include chlorotic ringspots, streaks, or altered flower shape and structure.
| Type of Plant Virus Symptoms | Examples |
|---|---|
| Leaf Symptoms | Leaf rust, powdery mildew, leaf spot, mosaic leaf patterns |
| Fruit Symptoms | Fruit spots, ringspots, mottling |
| Flower Symptoms | Chlorotic ringspots, necrotic ringspots, altered flower shape and structure |
Identifying and categorizing these different types of plant virus symptoms can aid in diagnosing specific viral diseases and implementing appropriate management strategies.
Understanding Viral Plant Pathogens
Plant viruses are submicroscopic pathogens that infect plant cells and disrupt their normal functions. These viruses can be transmitted through various means, including insect vectors, mechanical contact, pollen, seeds, or vegetative parts.
Once a plant is infected with a virus, it typically remains infected for its entire life. Understanding viral plant pathogens is crucial for preventing and managing viral infections in plants.
The Transmission of Plant Viruses
Viral plant pathogens can be transmitted by insects, such as aphids, which feed on plant sap and carry the virus from infected plants to healthy ones. Mechanical transmission occurs when sap from an infected plant comes into contact with a healthy plant, either through pruning, grafting, or other means.
Pollen, seeds, and vegetative parts can also carry viral pathogens and spread them to new plants. It’s important to be aware of these different modes of transmission in order to implement effective control measures.
Viral Infection in Plants
Once a plant is infected with a virus, it undergoes various changes that can have significant impacts on its growth and development. These changes can include leaf discoloration, deformity, stunting, and fruit or flower abnormalities.
The severity of the symptoms depends on the specific virus and the host plant. Some viruses have a narrow host range and only infect specific plant genera, while others have a broad host range and can infect a wide variety of herbaceous plants.
To effectively manage viral infections in plants, it is important to focus on prevention and early detection. This can be achieved through practices such as purchasing and planting certified virus-free or virus-resistant nursery stock, avoiding the grafting of infected plant parts onto healthy plants, and implementing proper sanitation measures to prevent the spread of viruses.
Controlling insect vectors can help reduce the transmission of viral pathogens. By understanding viral plant pathogens and implementing appropriate management strategies, gardeners and growers can minimize the impact of viral diseases on their plants.
| Viral Plant Pathogen | Transmission | Host Range |
|---|---|---|
| Apple mosaic virus | Insect vectors, mechanical transmission | Apple, pear, other fruit trees |
| Elm mosaic virus | Insect vectors, mechanical transmission | Elm |
| Hibiscus chlorotic ringspot virus | Insect vectors | Hibiscus, other ornamentals |
| Prunus necrotic ringspot virus | Insect vectors | Cherry, peach, plum |
| Tobacco mosaic virus | Insect vectors, mechanical transmission | Tobacco, tomato, other solanaceous plants |
| Turnip mosaic virus | Insect vectors, mechanical transmission | Cruciferous vegetables, ornamentals |
Common Viral Plant Diseases
When it comes to plant diseases, viruses are a common culprit. These submicroscopic pathogens can have a significant impact on the health and productivity of plants. It’s important for gardeners and growers to be aware of the common viral plant diseases so they can take proactive measures to prevent and manage them.
Examples of viral plant diseases include Apple mosaic virus, Elm mosaic virus, Hibiscus chlorotic ringspot virus, Prunus necrotic ringspot virus, Tobacco mosaic virus, and Turnip mosaic virus. Each of these viruses can cause different symptoms and affect a wide range of plant species.
For example, Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is known for causing mosaic patterns on leaves, stunting growth, and reducing fruit yield in a variety of plants. Apple mosaic virus (ApMV) can cause discoloration and deformities in apple trees, leading to reduced fruit quality.
Common Viral Plant Diseases
| Virus | Host Plants | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Apple mosaic virus | Apple, pear, cherry | Leaf discoloration, fruit deformity |
| Elm mosaic virus | Elm, zelkova | Leaf yellowing, leaf distortion |
| Hibiscus chlorotic ringspot virus | Hibiscus | Ring patterns, leaf chlorosis |
| Prunus necrotic ringspot virus | Peach, plum, cherry | Ring spots, leaf yellowing |
| Tobacco mosaic virus | Tobacco, tomato, pepper | Mosaic patterns, stunted growth |
| Turnip mosaic virus | Turnip, cabbage, cauliflower | Mottling, leaf distortion |
Identifying these common viral plant diseases and their associated symptoms is crucial for prompt management and prevention. Early detection and proper management practices, such as removing infected plants, controlling insect vectors, and implementing good sanitation practices, can help reduce the impact of viral diseases on plants.
By staying informed about the common viral plant diseases and taking proactive measures, gardeners and growers can protect their plants and ensure a healthy, productive garden or crop. Regular monitoring, proper sanitation, and disease-resistant plant varieties can all contribute to effective disease management.
Resources for Plant Disease Identification and Control
When it comes to managing plant diseases, having access to reliable resources for identification and control is crucial. Luckily, there are valuable resources available from reputable institutions that can help you in this endeavor.
One such resource is Michigan State University Extension. They offer a wealth of information on plant diseases, including fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases. Their publications cover a wide range of topics, providing you with detailed insights on disease identification and control strategies.
Another excellent resource is Ohio State University, which provides comprehensive information and services for diagnosing diseased plant samples. Their website offers factsheets, submittal forms, and details on sample submission and costs.
Whether you’re a gardener or a grower, accessing these resources can equip you with the knowledge necessary to effectively identify and manage plant diseases.
By taking advantage of these resources, you can enhance your understanding of plant disease identification and control. Armed with this knowledge, you’ll be better equipped to protect your plants and mitigate the impact of diseases.
Remember, prevention and early detection are key in maintaining healthy plants, so don’t hesitate to explore these valuable resources.
After reading this, check out our other articles on:
- Your guide to Fungal Plant Infections: Causes and Treatments
- Effective Bacterial Leaf Spot Natural Remedies for your Plants
FAQ
How can I recognize and identify plant virus symptoms?
Look for visible effects on plants such as color changes, shape deformities, or altered function. Learn to identify specific signs and symptoms of fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases. Consider other possibilities before concluding a plant has a virus.
What are some common symptoms of plant viruses on leaves?
Leaf symptoms can include discoloration, deformation, spotting, wilting, yellowing, crinkling, mosaic patterns, and stunting.
What are the symptoms of plant viruses on fruit?
Fruit symptoms can manifest as discoloration, deformity, spotting, ringspots, mottling, or the development of leaf-like structures.
How do plant viruses affect flowers?
Viral diseases can cause flower discoloration, deformation, spotting, alterations in shape or structure, chlorotic ringspots, necrotic ringspots, or the development of leaf-like structures on flowers.
How do I diagnose plant virus symptoms?
Diagnosing plant virus symptoms involves examining visible effects on plants, identifying specific signs and symptoms, and considering other factors such as abiotic diseases, herbicide injury, or nematode problems.
What can I do to manage plant virus symptoms?
While there is no cure or treatment for virus-infected plants in landscapes, proper cultural care can improve plant vigor. Purchase and plant high-quality, certified virus-free or virus-resistant nursery stock or seeds. Avoid grafting virus-infected plant parts onto healthy plants. Prevention and early detection are key.
What are the different types of plant virus symptoms?
Leaf symptoms, fruit symptoms, and flower symptoms are the main categories of plant virus symptoms.
How do viral plant pathogens spread?
Viral plant pathogens can be transmitted by insects, such as aphids, through feeding on plant sap, or mechanically through sap contact. They can also spread via pollen, seeds, or vegetative parts during propagation.
What are some common viral plant diseases?
Examples include Apple mosaic virus, Elm mosaic virus, Hibiscus chlorotic ringspot virus, Prunus necrotic ringspot virus, Tobacco mosaic virus, and Turnip mosaic virus.
Where can I find resources for identifying and controlling plant diseases?
Michigan State University Extension and Ohio State University offer publications, online information, and lab services for diagnosing diseased plant samples. Their websites provide resources on plant disease identification and control.






2 Comments
Comments are closed.